World TB Day “Yes! We Can End TB: Commit, Invest, Deliver”
Every year, 24 March is observed as World TB Day to amplify the urgency of ending tuberculosis (TB). This day is a crucial reminder of the global burden of TB and the ongoing challenges in prevention and care. It’s a call to strengthen political and social commitment, and to adopt a united approach to end TB. With international funding for TB shrinking in the current geopolitical climate, it’s more important than ever to rally support and ensure that we meet the goal of ending TB by 2030. The Finnish Lung Health Association (FILHA) study examines the LTBI situation in the Nordic-Baltic countries and Ukraine. Understanding the epidemiology, screening practices, and treatment regimens are crucial for effective management and control. The LTBI inventory study delves into the current state of TB and LTBI in our region, focusing on incidence variation, multidrug-resistant (MDR) TB, screening practices, and treatment protocols. The results of the study will be published later this year.
Latent Tuberculosis Infection Management in Nordic-Baltic Countries: Preliminary results of the Inventory
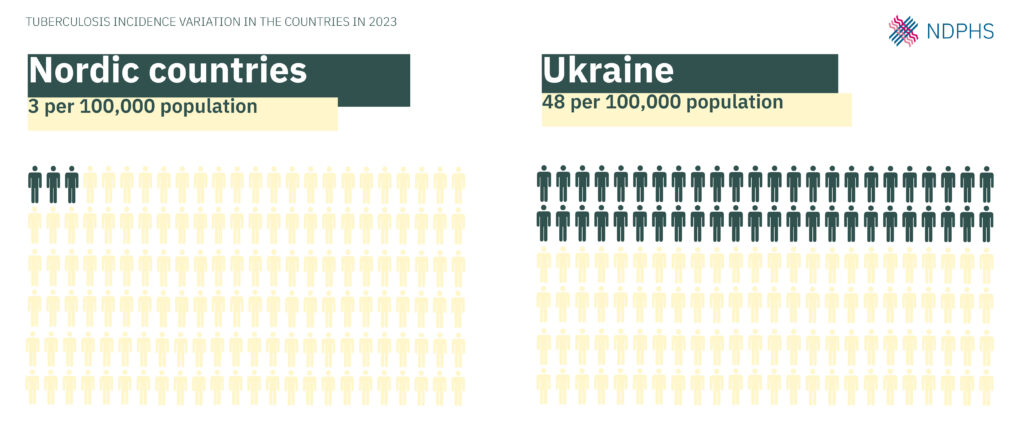
The incidence of TB varies significantly across Nordic-Baltic countries and Ukraine, influenced by socio-economic factors, healthcare infrastructure, and migration patterns. For example, in some countries over 85% of TB cases are among foreign-born individuals, highlighting the impact of migration on TB epidemiology.
Multidrug-resistant TB poses another significant problem in TB management due to its resistance to the most effective drugs. The high rates of drug resistance complicate treatment, further exacerbates the situation, and necessitate the development of robust management strategies.
Latent tuberculosis infection screening focus groups
Screening for LTBI is a critical component of TB control, aimed at identifying and treating latent infections before they progress to active disease. Nordic-Baltic countries have implemented various screening practices, often targeting high-risk groups such as contacts of TB patients, people living with HIV, and individuals undergoing immunosuppressive treatments. The World Health Organization recommends systematic screening for these groups, and we generally align with these guidelines. However, there is variability in the intensity and methods of screening.
Use of quantiferon in testing LTBI
The quantiferon test, an interferon-gamma release assay, is widely used in our region for diagnosing LTBI. It is preferred for its higher specificity compared to the Mantoux test and is particularly useful in populations with a high BCG vaccination against tuberculosis rate.
Most commonly used drug regimen in tuberculosis preventive treatment
Preventive treatment for LTBI is essential to reduce the risk of progression to active TB. The most commonly used regimens in the Nordic-Baltic countries include:
- 6 or 9 months of daily isoniazid
- 3 months of daily isoniazid plus rifampicin
- 3 months of weekly rifapentine plus isoniazid
These regimens are recommended regardless of HIV status and are aligned with WHO guidelines. However, the availability of drugs like rifapentine varies, with some ND countries being unable to obtain this medication, impacting the uniformity of TPT practices.
The management of LTBI in Nordic-Baltic countries involves navigating the complexities of varying TB incidence rates, high MDR-TB prevalence, diverse screening practices, and differing treatment regimens. By aligning with WHO recommendations and addressing the unique challenges faced by each country, Nordic-Baltic countries can enhance their TB control efforts and move closer to the ultimate goal of TB eradication.
Click here to read more about World TB Day and related events
Text: Mikko Vauhkonen and Iiris Rajalahti (Finnish Lung Health Association), NDPHS Expert Group on HIV, TB & Associated Infections
The Latent Tuberculosis Infections Inventory project aims to examine and create an overview of the Nordic-Baltic countries’ and Ukraine’s approaches to handling LTBI, and to compare those with the existing WHO and ECDC guidelines and recommendations. The project is financed by the Norwegian Ministry of Health and Care Services.
